The Complete Guide to DORA Compliance What It Means, Who It Impacts, and How to Achieve It
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is one of the most important regulatory shifts to affect the EU financial sector in recent years. Designed to strengthen ICT risk management and reduce disruption from cyber threats, the DORA regulation sets a new bar for digital resilience across financial institutions and their technology partners.
This guide breaks down the DORA framework in plain terms. You'll learn what the DORA Act requires, who must comply, key deadlines, and how to prepare using structured tools like GRC platforms. Whether you're a Chief Compliance Officer or part of an ICT vendor team, understanding DORA compliance is essential for protecting operations, avoiding penalties, and maintaining trust.

What Is the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA regulation) is a major part of the European Union’s Digital Finance Package. It was introduced by the European Commission to ensure that financial entities can withstand and recover from ICT-related disruptions — including cyberattacks, system failures, or data breaches.
DORA compliance focuses on more than just cybersecurity. It requires firms to build end-to-end digital resilience across their systems, teams, and service providers.
The regulation applies across EU member states and became law in January 2023. By January 2025, all in-scope organizations needed to be fully DORA compliant.
At its core, the DORA Act aims to protect the EU financial system from ICT risks that could lead to widespread instability. By standardizing digital risk management, incident reporting, testing, and vendor oversight, the DORA framework brings much-needed consistency to operational resilience practices across the industry.
Who Must Comply with DORA?
The DORA EU regulation applies to a wide range of organizations in the financial services ecosystem. These include:
- Banks and credit institutions
- Insurance and reinsurance firms
- Investment firms and brokers
- Crypto-asset service providers
- Payment institutions and e-money issuers
- Central counterparties and trading venues
- Crowdfunding platforms
- Management companies and AIFMs
In addition to financial entities, the Digital Operational Resilience Act also applies to ICT third-party service providers. This includes cloud service providers, data centers, software platforms, and managed services that support core financial functions.
If you offer digital infrastructure or applications to financial firms in the EU, you’re likely considered in scope under the DORA framework — even if your business is based outside the EU. This has made DORA compliance a top priority for global vendors supporting European markets.
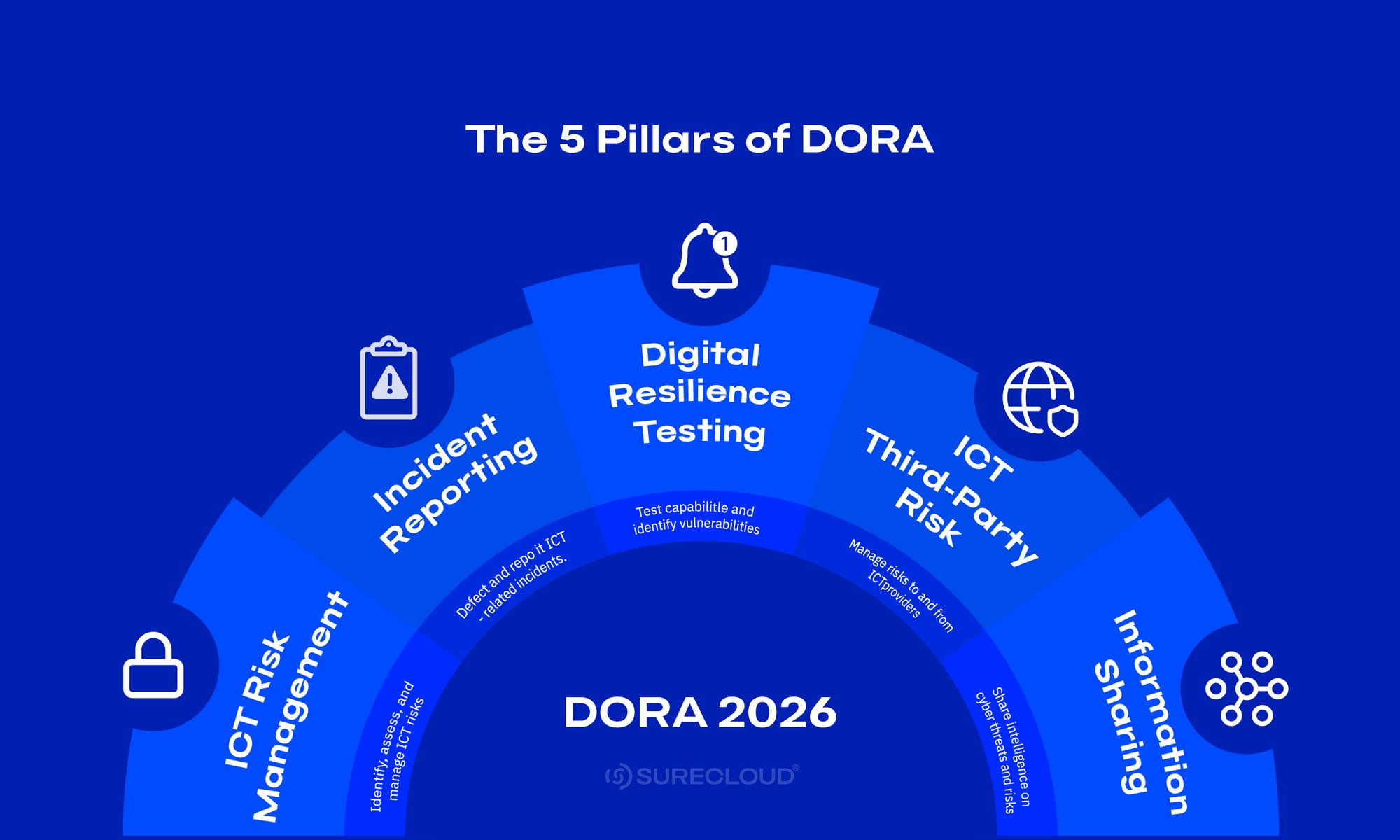
DORA’s Core Requirements Explained
To meet DORA compliance, organizations must implement structured processes across five core areas. Each pillar of the Digital Operational Resilience Act is designed to ensure financial stability, secure ICT operations, and improve cyber risk readiness.
ICT Risk Management Framework
Firms must adopt a formal ICT risk management framework that integrates with their enterprise risk strategy. This includes:
- Governance policies and clear accountability for ICT risk
- Identification, classification, and monitoring of ICT systems
- Regular risk assessments and control testing
- Documentation and oversight of internal and external ICT functions
Incident Reporting
Under the DORA regulation, significant ICT-related incidents must be reported within tight timelines. Requirements include:
- Reporting initial incidents to national competent authorities within 24 hours
- Submitting a detailed report within 72 hours
- A final follow-up report, no later than one month after resolution
DORA cybersecurity rules also require firms to keep internal logs, assess root causes, and share lessons learned. Reporting thresholds and formats will be harmonized across the EU.
Digital Operational Resilience Testing
To be considered digitally resilient under the DORA framework, firms must regularly test their ICT systems. This includes:
- Annual basic testing for most in-scope entities
- Advanced threat-led penetration testing (TLPT) every three years for entities performing critical functions
- Independent testing of backup systems, failover capabilities, and business continuity plans
These requirements are designed to ensure not just cybersecurity, but also operational readiness in the face of complex digital disruptions.
Third-Party Risk Management
DORA introduces new rules for monitoring ICT third-party providers. Financial entities must:
- Maintain an up-to-date register of all ICT-related contracts
- Include specific DORA-compliant clauses in vendor agreements
- Ensure providers follow robust security and continuity practices
- Build exit strategies to reduce reliance on a single provider
Unlike traditional due diligence, the Digital Operational Resilience Act imposes more active oversight, including potential inspections of critical ICT providers by EU authorities.
Information Sharing Arrangements
DORA encourages voluntary information-sharing on cyber threats and vulnerabilities. To remain compliant:
- Shared data must be relevant and focused on resilience
- Information-sharing arrangements must protect confidentiality and limit use
- Organizations should only engage in sharing networks that have clear governance and rules
This component of DORA supports collective defense against ICT risks across the EU financial sector.

How to Prepare for DORA: A Step-by-Step Framework
Achieving DORA compliance requires cross-functional effort — not just from compliance teams, but also from IT, risk, legal, and procurement. Here’s a practical roadmap to get ready:
Step 1 – Perform a Gap Analysis
Compare your current ICT controls and risk practices against DORA requirements. Use the five core pillars of DORA as your baseline, and identify gaps across:
- Risk frameworks
- Reporting workflows
- Testing programs
- Vendor oversight
- Governance documentation
A structured GRC platform can help accelerate this process.
Step 2 – Build a Compliance Task Force
Establish a cross-functional team involving:
- Risk and compliance leaders
- IT and infrastructure heads
- Legal and procurement representatives
- Business continuity and operations leads
Assign ownership to each of the DORA framework areas for faster execution.
Step 3 – Upgrade ICT Risk Management
Review and strengthen your ICT risk management policies. This may involve:
- Updating existing documentation
- Rolling out new risk assessments
- Training staff on DORA-related responsibilities
Be sure to align new controls with enterprise risk and governance models.

Compliance Timeline and Deadlines
DORA is already in force—as of January 17, 2025, all in-scope financial entities and ICT providers must be fully DORA compliant. Supervisory reviews and enforcement actions are now active.
Here’s a recap of key regulatory milestones:
December 27, 2022 – The DORA Act was published in the Official Journal of the European Union
January 16, 2023 – The regulation formally entered into force
January 17, 2025 – The final compliance deadline. All regulatory obligations now apply
From this point forward, organisations must demonstrate ongoing alignment with the DORA framework, including continuous monitoring, incident reporting, resilience testing, and third-party oversight. Failure to meet obligations can result in reputational harm, regulatory penalties, and service restrictions — especially for critical third-party providers.
How SureCloud Supports DORA Compliance
SureCloud helps financial entities and ICT providers operationalize DORA compliance through configurable GRC solutions built for evolving regulations.
Here’s how SureCloud maps to the five pillars of the Digital Operational Resilience Act:
ICT Risk Management
Use SureCloud’s risk framework builder to:
- Create, customize, and maintain DORA-compliant risk policies
- Map controls to the DORA framework and track remediation
- Align ICT risks with enterprise-level governance
Incident Response & Reporting
SureCloud simplifies DORA cybersecurity reporting with:
- Pre-built workflows to meet 24-hour and 72-hour deadlines
- Secure collaboration tools for multi-team input
- Customizable workflows to support national reporting formats
Digital Resilience Testing
Automate evidence tracking and testing schedules using:
- Built-in resilience assessment templates
- Support documentation of TLPT outcomes, including results and observations
- Action tracking tools to assign and monitor remediation across relevant teams
Third-Party Risk Management
SureCloud helps you manage vendor risk with:
- A centralized vendor register
- Automated due diligence workflows
- Contract expiry tracking aligned to DORA clauses
- Scoring and exit planning for critical providers
Information Sharing Readiness
Track participation in information-sharing groups, document controls on shared data, and maintain audit trails — all from a single platform.
Whether you’re a bank or a cloud vendor, SureCloud offers the best tools for framework compliance with built-in flexibility, audit support, and simplified governance.
How DORA Intersects With Other Frameworks
The Digital Operational Resilience Act does not exist in isolation. DORA compliance often overlaps with other key regulatory and security frameworks your organization may already follow. Understanding these relationships can reduce duplication and enhance overall resilience.
DORA vs. NIS2 vs. GDPR Comparison Table
|
Requirement Area |
DORA |
NIS2 |
GDPR |
EBA Guidelines |
|
Primary Focus |
Digital operational resilience in finance |
Cybersecurity for essential sectors |
Data privacy and protection |
ICT and security risk for financial entities |
|
Sector Coverage |
Financial institutions & ICT providers |
Essential/important entities (including some finance) |
All organisations handling EU personal data |
EU financial institutions |
|
Incident Reporting |
Yes – within 24 hours |
Yes – immediate & final reports |
Yes – within 72 hours for data breaches |
Yes – to national supervisors |
|
Third-Party Risk |
Yes – contract terms, exit plans, oversight |
Yes – for essential services |
Yes – if processors are involved |
Yes – part of ICT outsourcing monitoring |
|
Testing Requirements |
Yes – threat-led and resilience testing |
No specific testing mandate |
No |
Yes – security testing recommended |
|
Extra-EU Applicability |
Yes – applies to non-EU ICT vendors serving EU firms |
Yes – depending on service delivery |
Yes – if data subjects are in the EU |
Yes – if serving EU financial entities |
Overlap Opportunities
Several frameworks cover similar ground — especially in areas like incident response, vendor oversight, and governance. For example:
- Incident Reporting: DORA and GDPR both require fast reporting (24 and 72 hours respectively). A shared response plan can meet both.
- Vendor Risk: All frameworks expect robust oversight of third-party providers. Aligning reviews and controls reduces duplication.
- Governance: Unified policies can address requirements across DORA, NIS2, GDPR, and EBA Guidelines with fewer silos.
Risks of Non-Alignment
Treating these frameworks separately can lead to control gaps, inconsistent reporting, and duplicated tools. A unified approach improves efficiency and reduces the risk of missed obligations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is DORA regulation?
The DORA regulation — or Digital Operational Resilience Act — is an EU law requiring financial entities and their ICT providers to manage, test, and report on digital risk. It standardizes cybersecurity and resilience expectations across the financial sector.
Who enforces DORA?
DORA is enforced by the European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs), including the European Banking Authority (EBA), the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), and the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA).
What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Penalties vary by member state but may include administrative fines, reputational damage, and, for critical ICT providers, suspension of services to EU-based financial entities.
Is DORA compliance required for non-EU vendors?
Yes. If your ICT services support EU financial entities, you must meet DORA requirements. This includes cloud providers, data centers, and software vendors based outside the EU.
Does the Digital Operational Resilience Act apply in the UK?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act UK is not an official regulation. However, UK-based financial institutions that operate in the EU or serve EU clients must still meet DORA compliance requirements. UK regulators are also monitoring DORA closely as part of their broader cyber resilience strategy.
Next Steps: Building a Future-Ready Compliance Strategy
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) marks a major shift in how financial institutions and their ICT partners manage cyber risk. It raises the bar from basic security hygiene to comprehensive digital resilience — including proactive risk controls, rapid incident reporting, rigorous third-party oversight, and regular resilience testing.
DORA compliance isn’t just about meeting deadlines. It’s about protecting your organization, your customers, and the broader financial ecosystem from growing digital threats.
Whether you're a CISO, Risk Manager, or compliance lead, starting early gives you the best chance to build a practical, repeatable, and defensible approach.
Ready to take the first step?
Align with the DORA framework
Simplify ICT risk management
Automate incident workflows and reporting
Centralize third-party oversight
Stay DORA compliant at scale
Book a demo to see how SureCloud can support your DORA compliance journey — from policy to proof.
Explore all DORA Resources
"Excellent support team" We've been happy with the product and the support and communication has been excellent throughout the migration and onboarding process.
G2 - SureCloud
"Excellent support team" We've been happy with the product and the support and communication has been excellent throughout the migration and onboarding process.
G2 - SureCloud
"Excellent support team" We've been happy with the product and the support and communication has been excellent throughout the migration and onboarding process.
G2 - SureCloud
"Excellent support team" We've been happy with the product and the support and communication has been excellent throughout the migration and onboarding process.
G2 - SureCloud
"Excellent support team" We've been happy with the product and the support and communication has been excellent throughout the migration and onboarding process.
G2 - SureCloud
.png)








_HighPerformer_Enterprise_HighPerformer.png)