ISO 42001 Certification: Process, Timeline & Costs Explained
ISO 42001 is the world’s first AI management system standard. It gives your organization a clear way to govern AI, manage risk, and show responsible practice as AI use grows.
ISO 42001 certification turns that intent into an auditable system. It helps you prove you have consistent processes, clear ownership, and evidence that holds up in an audit.
With key EU AI Act obligations rolling out through 2025 and 2026, more organizations are under pressure to show how they manage AI risk, oversight, and documentation. For many teams, ISO/IEC 42001 certification is a practical path to stronger EU AI Act alignment, clearer AI compliance standards, and better AI trust assurance.
What this guide covers:
- What ISO 42001 certification means and what “ISO 42001 certified” signals
- The ISO 42001 certification process, step-by-step
- A realistic ISO 42001 certification timeline for 2025 to 2026
- Key ISO 42001 certification cost drivers and hidden effort
- What auditors expect and where technology support helps
.webp)
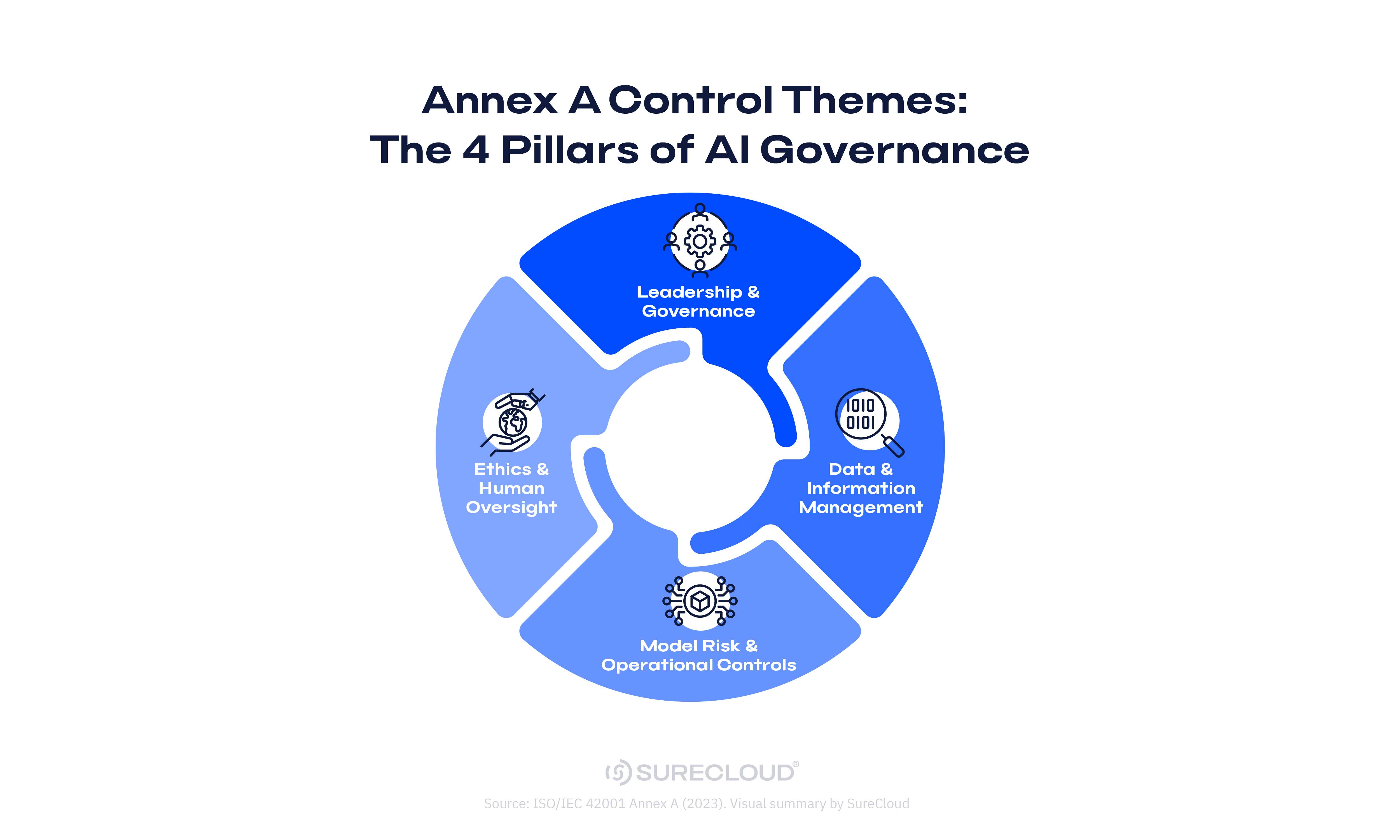
What ISO 42001 Certification Means
ISO 42001 certification is a management system certification, not product approval. It does not certify a specific AI model, vendor, or tool. It certifies the management system your organization uses to govern AI across its lifecycle.
That includes how you define accountability, identify risk, implement controls, monitor performance, and improve over time. In practice, it is an AI governance certification focused on repeatability and evidence.
What “ISO 42001 certified” Actually Signals
Being ISO 42001 certified typically signals that your organization can:
- Define the scope of AI use and oversight
- Operate a consistent AI governance framework across teams
- Identify and manage AI risk in a structured way
- Maintain evidence that controls are designed, implemented, and reviewed
- Demonstrate continuous improvement, not one-time compliance
Who Can Certify You?
ISO does not issue certificates. Certification is issued by independent certification bodies, using accredited auditors, to assess your management system against ISO/IEC 42001 requirements.
How To Get ISO 42001 Certified: The Process
ISO 42001 certification follows a clear, repeatable path. The steps below explain what to expect at each stage, what evidence auditors look for, and how to stay on track through the certification process.
The Step-by-Step Certification Process
|
Stage |
Description |
Deliverables |
SureCloud Support |
|
1. Gap Assessment |
Review current state against Annex A controls and scope |
Readiness report, scoped AI inventory, prioritized remediation plan |
Pre-assessment templates in SureCloud |
|
2. System Design and Implementation |
Build and roll out your AI governance framework |
Policies and processes, role accountability, AI risk register structure, control mappings |
GRC workflows for AI risk classification |
|
3. Internal Audit |
Check controls are operating as designed |
Audit evidence, findings log, corrective actions, management review inputs |
AI risk dashboard and controls library |
|
4. Certification Audit (Stage 1 and 2) |
External review by the certification body |
Audit report and decision |
SureCloud evidence pack automation |
|
5. Ongoing Surveillance and Recertification |
Maintain controls and improve over time |
Review logs, improvement actions, surveillance audit readiness |
Continuous monitoring in platform |
What Auditors Tend to Focus on
Audits rarely come unstuck because a document is missing. More often, issues arise when evidence cannot be produced or processes are not operating consistently.
Auditors typically want to see:
- A defined scope with clear governance roles and decision rights
- A consistent way to classify AI systems and manage risk
- Evidence that Annex A controls operate in practice, not only on paper
- A review cadence with management oversight and change history
- Corrective actions tracked through to closure
Auditor Expectations vs Technology Support
Technology does not replace governance. It can reduce manual effort and help teams run workflows, reporting, and evidence collection at scale through GRC platform automation.
|
What Auditors Typically Expect: |
How Technology Can Support It: |
|
Defined scope, accountability, and approvals |
Centralized workflows, role tracking, and sign-offs |
|
Documented controls mapped to risk |
Control libraries, mappings, and structured registers |
|
Evidence that controls are operating |
Linked artifacts, audit trails, and evidence packs |
|
Consistent risk classification and reporting |
Standard scoring, dashboards, and exportable reports |
|
Regular reviews and continuous improvement |
Review reminders, version history, and action tracking |
Timeline to Certification (2025 to 2026 Reality Check)
Your ISO 42001 certification timeline depends on readiness more than ambition. The biggest drivers are AI system complexity, existing ISMS maturity, and resource availability.
Typical duration by organization type:
- SME: 4–6 months
- Enterprise: 6–12 months
Readiness Indicators That Influence Your ISO 42001 Certification Timeline
You are more likely to hit the shorter end of the range when:
- You have an inventory of AI use cases with responsible owners
- Governance roles and decision rights are already defined
- You run internal audits and management reviews on a cadence
- Evidence collection is centralized or consistently managed
- Risk and control mappings are already used for reporting
Timelines tend to extend when:
- AI use is decentralized and scope needs alignment across units
- Control ownership and review cadence are not yet established
- Evidence sits across multiple tools with limited audit trail consistency
- Internal audit and corrective action routines are still maturing
Certification Roadmap View For Planning
Example checkpoints to reflect in the roadmap:
- Q1: Scope, gap assessment, implementation plan
- Q2: Control implementation, evidence design, initial internal audit
- Q3: Stage 1 audit prep, remediation, Stage 2 audit readiness
- Q4: Certification decision, surveillance planning, continuous improvement cycle
Cost Considerations
ISO 42001 certification cost is shaped by scope, audit effort, and internal time. Your total investment is usually a mix of external fees and the effort required to implement, test, and maintain the system. Costs also vary by certification body and geography.
Typical ranges are approximate:
- Pre-assessment or gap analysis: £5–10k
- Implementation support: £15–30k
- External audit: £10–20k per cycle
What Sits Behind ISO 42001 Certification Cost
Costs tend to increase when:
- More AI systems are in scope
- More sites, teams, or third parties are involved
- Evidence collection is manual or inconsistent
- Internal audit and management review processes are immature
Costs tend to be easier to control when:
- Scope is clear and defensible
- Controls are mapped to risk with consistent ownership
- Evidence requirements are designed early
- Reporting is standardized and repeatable
What Drives Audit Days
Certification bodies typically estimate audit effort based on factors like:
- Scope breadth and number of AI lifecycle processes in scope
- Number of operating locations
- Outsourced or third-party activities that require oversight evidence
- Complexity of governance and decision-making structure
- Maturity of documentation and evidence availability
Hidden Costs to Budget For
Hidden costs typically include:
- Staff training and awareness
- Evidence collection and internal testing
- Annual maintenance, surveillance preparation, and corrective actions
Cost breakdown table
These ranges can overlap, but enterprises typically land at the higher end due to broader scope and the extra days and evidence sources required for audits.
| Cost Element | Typical SME range | Typical Enterprise range |
Notes |
|
Pre-assessment or gap analysis |
£5–10k |
£5–10k |
Varies by scope and readiness |
|
Implementation support |
£15–30k |
£15–30k |
Driven by complexity and number of AI systems in scope |
|
External audit |
£10–20k per cycle |
£10–20k per cycle |
Audit days increase with scope and complexity |
|
Internal time and enablement |
Variable |
Variable |
Training, evidence, internal audits, and maintenance |
How GRC Software Can Reduce Audit Effort
Even when external fees are fixed, internal effort can drop when evidence and reporting are structured. This is where GRC platform automation can reduce time spent chasing documentation across teams.
A platform can help you:
- Standardize risk and control mappings
- Track ownership and review cadence
- Centralize evidence for faster audit preparation
- Reduce manual reporting cycles as requirements evolve
ISO 42001 and the EU AI Act: Dual Value
Many organizations pursue ISO 42001 certification as part of their EU AI Act preparation. That’s because many Annex A control themes overlap with expectations that commonly apply to high-risk AI systems, especially around governance, risk management, oversight, monitoring, and documentation.
This section is practical planning guidance, not legal advice. Certification is not an exemption. For many organizations, it also provides a proactive compliance defense by strengthening governance and making evidence easier to produce when required.
How to Use the ISO 42001 and EU AI Act Alignment Table
The table below supports planning and budgeting by helping you:
- Identify overlap between your AI governance framework and regulatory obligations
- Budget for the evidence and operational work required to maintain compliance
- Structure internal reporting, so controls and evidence can be surfaced quickly
|
ISO 42001 Annex A theme |
Typical overlap with EU AI Act obligations |
Evidence you may need |
|
AI risk management |
Risk assessment, mitigation planning, ongoing review |
Risk register entries, scoring methodology, review logs |
|
Data governance |
Data quality and governance processes |
Data governance policies, data quality checks, documentation records |
|
Transparency and information |
Documentation and communications for oversight and stakeholders |
Documentation packs, change logs, stakeholder information templates |
|
Human oversight |
Defined oversight roles and escalation paths |
Role definitions, approvals, incident escalation records |
|
Monitoring and improvement |
Continuous review, incident learning, improvement actions |
Monitoring reports, corrective action tracking, management review minutes |
|
Records and evidence |
Documentation to support accountability and auditability |
Evidence repository, audit trails, internal audit reports |
How SureCloud Supports the Journey
Certification is easiest when you can prove three things consistently:
- Controls are defined
- Controls are operating
- Evidence is available on demand
SureCloud supports your AI compliance journey through:
- Pre-built AI governance templates and control mappings
- Automated AI risk classification and Annex A reporting
- Advisory support for audit readiness and continuous compliance
This supports AI governance certification by reducing manual effort and keeping evidence organized as your scope grows.
What You Can Centralize to Reduce Effort
A structured approach reduces time spent chasing evidence across tools and teams. A central platform can help you maintain a single view of:
- AI inventory and scope boundaries
- AI risk register and control mappings
- Ownership, actions, and review cadence
- Audit evidence and supporting documentation
- Reporting views for leadership and audit preparation
FAQ’s
How long does ISO 42001 certification last?
Certification bodies typically operate a multi-year certification cycle with surveillance audits. Your certification body will confirm the cycle and surveillance approach.
Who issues the certificate?
Certificates are issued by independent certification bodies, not by ISO. The audit is completed by ISO-accredited auditors working through the certification body.
Is certification mandatory under the EU AI Act?
Certification is not typically mandatory. It can strengthen your evidence and governance posture, but EU AI Act obligations still apply based on how your AI systems are classified and used.
Can we certify only part of our organization?
Yes, scope can be defined, but it must have clear boundaries and supporting evidence. Your certification body will review and confirm whether the scope is appropriate.
How does ISO 42001 interact with ISO 27001 or ISO 9001?
Many organizations align ISO/IEC 42001 certification with existing management systems. If you already operate ISO 27001 or ISO 9001 practices, you can often reuse governance routines, internal audit discipline, and continuous improvement cycles.
Next Steps for ISO 42001 Certification
ISO 42001 certification is not just a badge. It is proof that AI is managed responsibly and transparently through a repeatable management system.
With 2026 high-risk AI obligations looming, becoming ISO 42001 certified can help you demonstrate consistent governance for high-impact use cases and make your AI compliance journey easier to run and easier to evidence.
If you want to understand your ISO 42001 certification timeline, your ISO 42001 certification cost drivers, and the most efficient ISO 42001 certification process for your scope, the next step is a readiness conversation.
“In SureCloud, we’re delighted to have a partner that shares in our values and vision.”
Read more on how Mollie achieved a data-driven approach to risk and compliance with SureCloud.

.png)



.jpg)
.jpg)